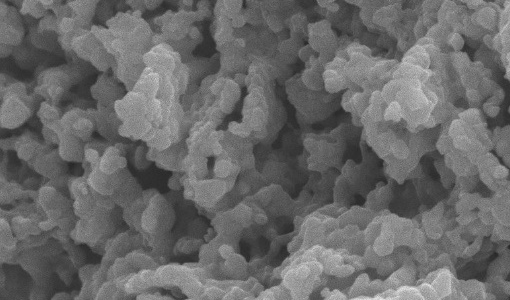
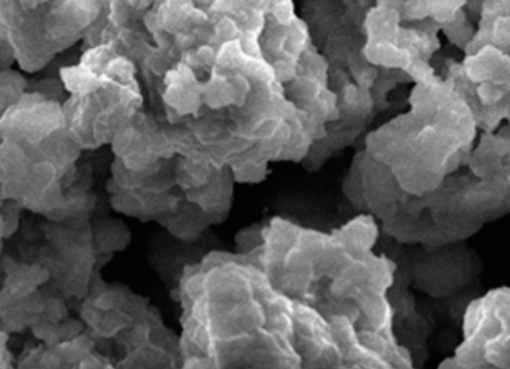
This study performed both macroscopic and microscopic investigation to determine the interaction mechanism for heavy metal adsorption on functionalized MCM-41 mesoporous silica. Hybrid sorbent material has been developed by modifying MCM-41 with sodiumdodecylsulphate (SDS), named as SDS-MCM-41, and tested for capturing Cu2+ and Zn2+ in the solution. Zeta potentials of pristine MCM-41, SDS-MCM-41, and the adsorbents that adsorbed Cu2+ and Zn2+ for different pHs and initial metal ion concentrations were employed to estimate macroscopically the adsorption ability. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation was performed to investigate adsorption behavior in microscopic point of view. Zeta potential and molecular simulation reveal that SDS functional groups are responsible for the adsorption of metal ions through the interaction between the anionic charged surface of SDS-MCM-41 and the cationic metal ions. The qualitatively consistent results of molecular dynamics simulations with experiments suggest the possibility of applying computer simulation for preliminarily selection of adsorbent functional groups for removal of Cu2+ and Zn2+.
The adsorption aspect of Cu2 + and Zn2 + on MCM-41 and SDS-modified MCM-41

Related tags :
S. Wongsakulphasatch
Related Articles
October 30, 20210
Dr. S. Wongsakulphasatch
Heavy metal adsorption by porous solids
Materials and systems for CO2 capture
Hydrogen production
Colloid and interface science
Process Integration
Analytical Science
Dr. Won
Read More
May 4, 20200
Bi-metallic CuO-NiO based multifunctional material for hydrogen production from sorption-enhanced chemical looping autothermal reforming of ethanol
Bi-metallic CuO-NiO based multifunctional materials were developed and employed for H2 production via sorption-enhanced chemical looping autothermal reforming (SE-CLAR) of ethanol. The effects of addi
Read More
August 31, 20200
SDS modified mesoporous silica MCM-41 for the adsorption of Cu2+, Cd2+, Zn2+ from aqueous systems
SDS-functionalized mesoporous silica MCM-41, was synthesized and used as adsorbent for remediating toxic metal contamination. The new material was applied to capture the heavy metal ions Cu2+, Cd2+, a
Read More
May 4, 20210
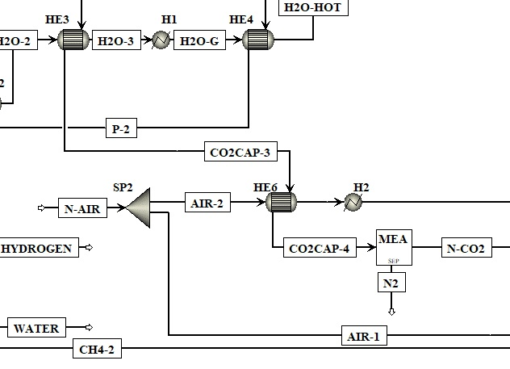
Optimisation of a Sorption-Enhanced Chemical Looping Steam Methane Reforming Process
An intensified hydrogen production steam reforming process named ‘Sorption-Enhanced Chemical Looping Steam Methane Reforming’ (SE-CL-SMR) was studied. Aspen Plus was used to carry out a thermodynamic
Read More
June 4, 20160
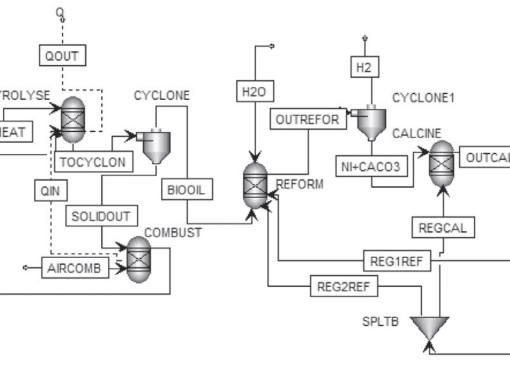
Performance evaluation of sorption enhanced chemical-looping reforming for hydrogen production from biomass with modification of catalyst and sorbent regeneration
Process simulation of sorption enhanced chemical-looping reforming for hydrogen production from biomass was investigated. Corn stover was converted to bio-oil via pyrolysis prior to sorption enhanced
Read More
May 3, 20190
Influence of CaO precursor on CO2 capture performance and sorption-enhanced steam ethanol reforming
This work presents the effect of calcium and carbonate precursors on properties of CaCO3. The synthetic CaCO3 samples were transformed into CaO and tested their application to high-temperature CO2 cap
Read More
May 4, 20130
Comparative study of fuel gas production for SOFC from steam and supercritical-water reforming of bioethanol
Theoretical study of fuel gas (H2 & CO) production for SOFC from bioethanol was carried out to compare performances between two reforming technologies, including steam reforming (SR) and supercrit
Read More
July 30, 20160
Effect of Fe open metal site in metal-organic frameworks on post-combustion CO2 capture performance
Iron open metal site in metal-organic frameworks, MIL-88A and MIL-127(Fe), was tested to investigate its performance on CO2 separation from a binary mixture CO2/N2 under simulated post-combustion syst
Read More