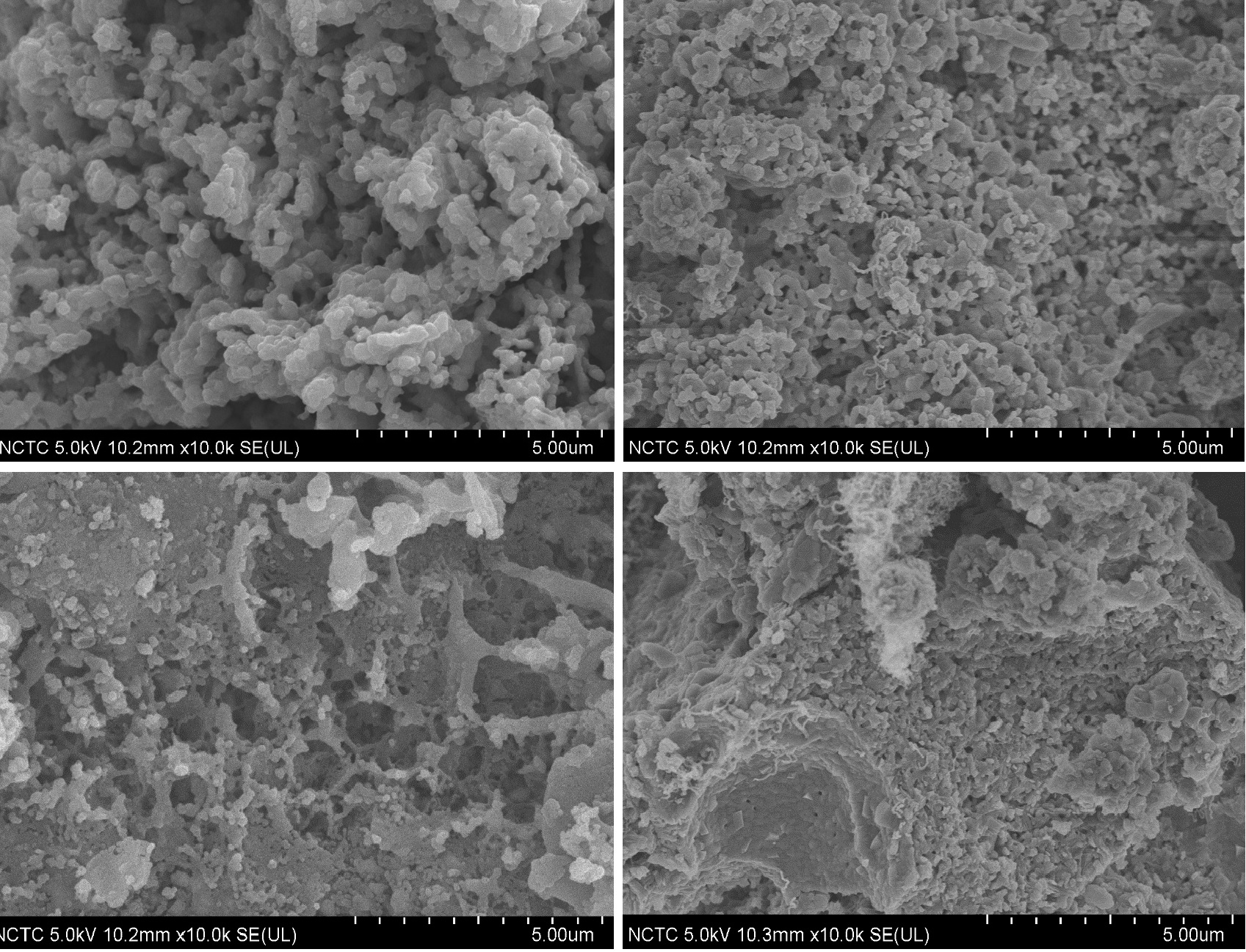
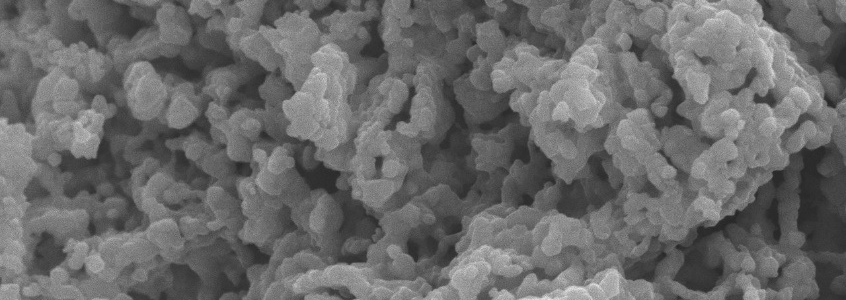
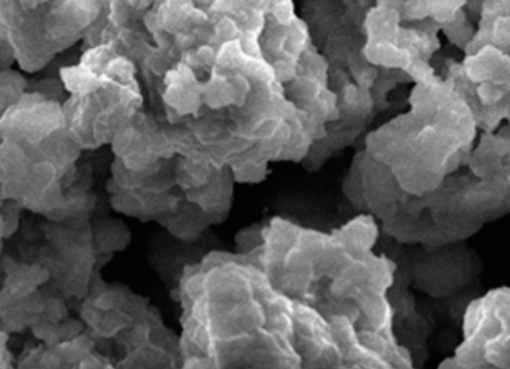
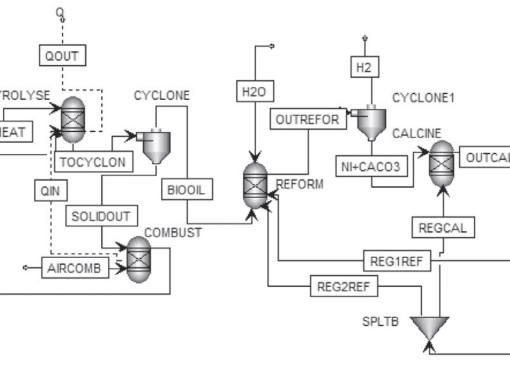
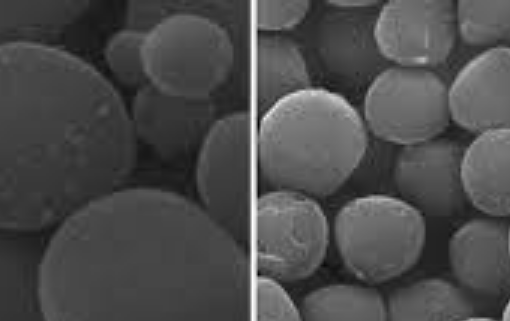
Bi-metallic CuO-NiO based multifunctional materials were developed and employed for H2 production via sorption-enhanced chemical looping autothermal reforming (SE-CLAR) of ethanol. The effects of adding copper oxide (CuO) as a co-oxygen carrier and material preparation method on H2 production performances, including activity, reusability, and energy penalty, were studied. The results revealed that adding CuO into one-body multifunctional material provided positive impacts on H2 production performances. The use of multifunctional material could reduce reforming temperature to milder temperature at 500 °C. The key finding is that position of CuO in the multifunctional material showed a significant effect. Placing of CuO on the surface could enhance catalytic property whereas placing NiO closed to CaO could reduce heat for CaO regeneration. For the SE-CLAR operating temperature at 500 °C and steam to ethanol ratio (S/E) = 3, impregnation of NiO on the surface of homogeneous CuO-CaO-Ca12Al14O33, NiO/CuO-CaO-Ca12Al14O33, produced 83% H2 purity for 30 min while impregnation of CuO on the surface of homogeneous NiO-CaO-Ca12Al14O33, CuO/NiO-CaO-Ca12Al14O33, produced 89% H2 for 45 min. Sol-gel one-pot synthesis method of NiO-CuO-CaO-Ca12Al14O33 produced 91% H2 purity for 60 min. Complete regeneration temperature of CaO was achieved at 800 °C, which accounts for 14% thermal energy reduction for the CuO/NiO-CaO-Ca12Al14O33. The NiO/CuO-CaO-Ca12Al14O33 could maintain its performance on producing high H2 purity for at least five consecutive operating cycles.